
Key messages
- Illicit drugs can have effects on your brain and body. This includes your mouth.
- Common effects include tooth grinding, a dry mouth, tooth decay and gum disease.
Illicit drugs are associated with a range of physiological and behavioural effects. These effects can cause damage to the health of your mouth. In general, effects can include:
- tooth grinding
- a decrease in saliva causing a dry mouth
- tooth decay
- gum disease.
If you are a regular user of illicit drugs, it is important to have a check-up with your dentist to check for any damage to your teeth or gums. Make sure you tell your dentist about any illicit drugs that you use. Your dentist will not share this information but knowing this can help them to look after your teeth and mouth.
Marijuana
Marijuana/cannabis use can cause:
- an increase in appetite
- a decrease in the amount of saliva in the mouth causing a dry mouth
- users to have poorer oral hygiene.
Together these factors can increase your risk of developing tooth decay. Smoking marijuana is also associated with an increased risk of developing oral cancer.
Methamphetamine
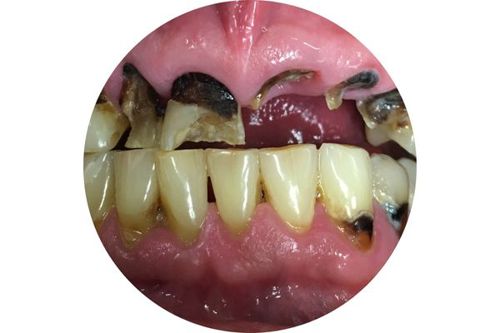
Regular users of methamphetamine (meth or ice) often experience large amounts of tooth decay. This is often called 'meth mouth'. This tooth decay is due to the drug causing:
- a decrease the amount of saliva in the mouth
- cravings for sugary and carbonated drinks
- tooth grinding or clenching
- long periods of poor oral hygiene.
It is recommended that you delay dental treatment for a minimum of six hours after you take methamphetamine.
Cocaine
Cocaine use can cause you to grind or clench your teeth. This can casue your teeth to wear down. Rubbing cocaine directly on the gums can cause ulcers or the gums to wear away.
It is recommended that you delay dental treatment for six to 24 hours after taking cocaine.
Heroin
Regular users of heroin and methadone can experience large amounts of tooth decay and gum disease. This is because of a decrease in the amount of saliva your mouth makes and generally poor oral hygiene.


